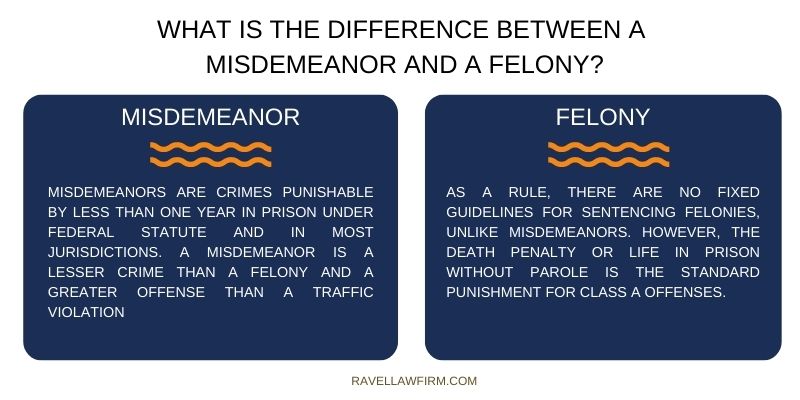
Felony and misdemeanor law forms the bedrock of our criminal justice system, defining the severity of offenses and shaping the consequences for those who violate the law. This intricate system categorizes crimes based on their nature and impact, with felonies representing the most serious offenses, carrying potentially life-altering consequences, while misdemeanors are less severe and typically result in lighter penalties.
Understanding the nuances of felony and misdemeanor law is crucial for individuals, communities, and the legal system as a whole. This knowledge empowers individuals to navigate the complexities of the law, promotes responsible citizenship, and informs policy decisions aimed at achieving justice and public safety.
The Criminal Justice System and Sentencing

The criminal justice system is a complex process that involves various stages, from the initial arrest to the final sentencing. This system aims to ensure fairness and accountability for individuals accused of crimes while protecting the rights of victims and society as a whole. The system’s effectiveness relies heavily on the roles of key players, including prosecutors, defense attorneys, and judges, who work together to ensure a just outcome.
Also Read
Stages of the Criminal Justice System, Felony and misdemeanor law
The criminal justice system operates in a series of distinct stages, each with specific procedures and legal considerations. The stages are:
- Arrest: This is the initial stage where an individual is apprehended by law enforcement officers based on probable cause.
- Booking: Following the arrest, the suspect is brought to a police station for processing, including fingerprinting, photographing, and recording personal information.
- Initial Appearance: Within a short period after arrest, the suspect is brought before a judge for an initial appearance. At this stage, the charges are read, bail is set, and the suspect is informed of their rights.
- Preliminary Hearing: This hearing determines whether there is sufficient evidence to proceed with the case. The prosecution presents evidence, and the defense may cross-examine witnesses.
- Indictment or Information: If there is enough evidence, the prosecution will formally charge the suspect with a crime through an indictment (grand jury) or information (prosecutor’s filing).
- Arraignment: The suspect is formally presented with the charges and asked to enter a plea (guilty, not guilty, or no contest).
- Discovery: Both the prosecution and defense exchange information and evidence related to the case. This stage allows both sides to prepare their strategies.
- Trial: If the case does not result in a plea bargain, a trial will be held. The prosecution presents evidence to prove the defendant’s guilt beyond a reasonable doubt, while the defense presents evidence to challenge the prosecution’s case.
- Sentencing: If the defendant is found guilty, the judge will impose a sentence based on the severity of the crime, the defendant’s criminal history, and other relevant factors.
Roles of Key Players
The criminal justice system relies on the coordinated efforts of several key players, each with distinct responsibilities:
- Prosecutors: The prosecution team represents the government and is responsible for bringing charges against the accused. Their role is to present evidence and argue for the defendant’s guilt.
- Defense Attorneys: Defense attorneys represent the accused and work to protect their rights throughout the legal process. They investigate the case, gather evidence, and present arguments in defense of their client.
- Judges: Judges preside over legal proceedings, ensure fairness, and make rulings on legal issues. They are responsible for setting bail, overseeing trials, and imposing sentences.
Sentencing Options
Sentencing options for felonies and misdemeanors vary depending on the nature of the crime, the defendant’s criminal history, and the judge’s discretion. Some common sentencing options include:
- Probation: This involves supervised release into the community, with conditions such as drug testing, counseling, and community service.
- Community Service: This involves performing unpaid work for the benefit of the community, often as a form of restitution or rehabilitation.
- Incarceration: This involves imprisonment in a jail or prison for a specific period of time. Incarceration is typically reserved for more serious offenses and may be accompanied by other penalties, such as fines or restitution.
Impact of Felonies and Misdemeanors on Society: Felony And Misdemeanor Law
The consequences of felony and misdemeanor convictions extend far beyond the individual, impacting families, communities, and society as a whole. These convictions can lead to significant social and economic challenges, affecting employment, housing, and access to essential services.
Social and Economic Consequences
The stigma associated with a criminal record can create significant barriers to reintegration into society. Individuals with felony convictions often face challenges finding employment, housing, and even accessing basic necessities like healthcare. This can lead to a cycle of poverty and social exclusion, making it difficult for individuals to rebuild their lives and contribute to society.
- Employment: Many employers are hesitant to hire individuals with felony convictions, limiting their employment opportunities. This can lead to financial instability and a lack of economic independence.
- Housing: Some landlords refuse to rent to individuals with felony convictions, making it difficult to find stable housing. This can lead to homelessness and instability, further compounding the challenges faced by formerly incarcerated individuals.
- Access to Services: Felony convictions can impact access to government assistance programs, such as food stamps and healthcare, further exacerbating economic hardship and limiting opportunities for social mobility.
Impact of Incarceration on Individuals, Families, and Communities
Incarceration has a profound impact on individuals, families, and communities. The separation of family members due to incarceration can have long-lasting consequences, particularly for children. Incarceration can also disrupt social networks and contribute to community instability.
- Individuals: Incarceration can lead to a loss of personal liberty, social connections, and economic opportunities. It can also have a negative impact on mental and physical health.
- Families: The separation of family members due to incarceration can have a significant emotional and financial impact on families. Children of incarcerated parents often face challenges in school, have higher rates of behavioral problems, and are more likely to be involved in the criminal justice system themselves.
- Communities: High rates of incarceration can contribute to community instability and crime. Incarceration can also have a negative impact on the local economy, as it removes individuals from the workforce and can lead to a loss of tax revenue.
Recidivism Rates and Challenges Faced by Formerly Incarcerated Individuals
Recidivism rates, which measure the percentage of individuals who are rearrested after release from prison, are a significant concern. High recidivism rates highlight the challenges faced by formerly incarcerated individuals in successfully reintegrating into society.
- Recidivism Rates: Studies have shown that recidivism rates are high, indicating that many individuals who are released from prison are likely to return to the criminal justice system. This is often attributed to factors such as lack of employment opportunities, limited access to education and job training, and lack of support services.
- Challenges Faced by Formerly Incarcerated Individuals: Formerly incarcerated individuals face a range of challenges, including finding employment, housing, and accessing healthcare. They may also struggle with mental health issues, substance abuse, and social isolation.
The distinction between felonies and misdemeanors underscores the intricate balance between individual rights and societal safety. By understanding the principles governing these categories, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of the criminal justice system and its impact on individuals and society at large. As we move forward, it is imperative to engage in thoughtful discussions about the effectiveness of our legal framework, explore innovative approaches to rehabilitation, and strive to create a more just and equitable system for all.
Felony and misdemeanor law are essential components of the legal system, defining the severity of crimes and the potential consequences for offenders. These classifications play a crucial role in consumer protection, as violations of Consumer protection regulations can often be categorized as misdemeanors or even felonies, depending on the nature and extent of the violation. Understanding the legal framework surrounding consumer protection is vital for both businesses and consumers, ensuring fair practices and safeguarding the rights of all parties involved.




